Business leaders face constant pressure to make faster, smarter decisions than competitors. The OODA Loop, Observe, Orient, Decide, Act, offers a battle-tested framework that transforms chaotic information into decisive action. Originally developed for aerial combat, this strategic tool now gives businesses a competitive edge in rapidly changing markets.
This article unpacks how to implement the OODA Loop in your organization with practical examples from various industries.
You’ll discover common pitfalls to avoid and specific techniques to accelerate your decision cycles. The companies that master this framework consistently outmaneuver competitors even with fewer resources.
What is the OODA Loop?
The OODA Loop is a decision-making framework created by Air Force Colonel John Boyd during the Korean War to help pilots make split-second decisions in combat. It stands for Observe, Orient, Decide, and Act, a continuous cycle that prioritizes speed and adaptability over perfect information. Boyd noticed that pilots who completed this cycle faster consistently outmaneuvered opponents, even when flying technically inferior aircraft.
This military strategy translates remarkably well to business, where companies face similar high-stakes decisions under pressure and uncertainty. Smart business leaders now use this framework to process information quickly, adapt to changing conditions, and take decisive action before competitors can respond.
Related: OODA Loop vs. PDCA Cycle
Breaking Down the OODA Loop: Four Steps to Faster Business Decisions
The OODA Loop isn’t complicated, but mastering each phase requires discipline and practice. Let’s examine how each component works in practical business situations.
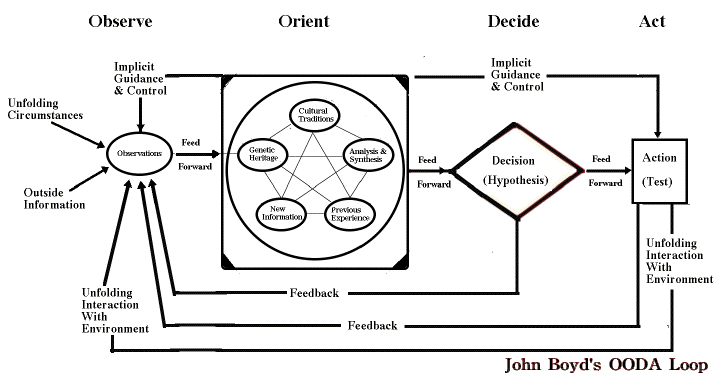
Step 1: Observe
The Observe phase requires collecting unfiltered data about your market, customers, and competitors without jumping to conclusions. Smart leaders establish systematic intelligence gathering across multiple channels, from sales conversations to social listening and competitor analysis. This stage demands ruthless honesty about what’s actually happening rather than what you hope or assume is happening.
The quality of your decisions can only be as good as the information you gather at this stage. Companies that excel at observation create formal processes to capture valuable intelligence from frontline employees who interact with customers daily. Organizations like Amazon and Toyota deliberately structure their teams to maximize the flow of unbiased information to decision-makers.
Step 2: Orient
Orientation transforms raw data into meaningful insights by filtering information through your unique business context and experience. Your company culture, historical knowledge, and industry perspective all create the lens through which you interpret observations. This critical cognitive step separates successful business leaders from those who fail to adapt to changing conditions.
Orientation requires regular reassessment of assumptions as new information emerges. Netflix originally oriented itself as a DVD-by-mail company before recognizing the shift toward streaming content based on customer behavior data. The most adaptive organizations deliberately seek diverse perspectives during this phase to avoid confirmation bias and spot emerging patterns before competitors.
Step 3: Decide
The Decision phase involves choosing a course of action based on your oriented observations, even with incomplete information. Fast decision-making often beats perfect decision-making in competitive markets where opportunities appear and disappear quickly. Truly effective leaders develop clear decision frameworks that prevent analysis paralysis.
Amazon uses a “Type 1/Type 2” decision framework that distinguishes between reversible decisions (made quickly) and irreversible ones (requiring more deliberation). Companies that excel at this stage maintain forward momentum by making smaller, frequent decisions rather than waiting for perfect data. They establish clear accountability and time limits for decisions at every level of the organization.
Step 4: Act
Action represents the execution of your decision and provides the feedback needed to restart the OODA Loop. The most effective organizations act with conviction while remaining ready to adjust based on results. Without decisive action, even the best analysis becomes worthless in rapidly changing business environments.
The Act phase includes measuring outcomes and communicating results throughout the organization. Companies that successfully implement the OODA Loop, like Zara in fashion retail, create systems for rapid testing and iteration that continuously feed new observations back into the cycle. Their advantage comes from completing multiple OODA cycles while competitors are still analyzing options.
10 Practical Steps to Implement the OODA Loop in Business
Implementing the OODA Loop requires more than understanding the concept. These practical steps will help you integrate this powerful framework into your daily business operations.
1. Identify Your Decision Domains
Start by identifying specific business areas where faster decisions would create competitive advantage. Focus on domains with frequent changes, significant competitive pressure, or rapid customer preference shifts. Applying OODA principles to these targeted areas first will demonstrate value before expanding to broader business functions.
2. Build Robust Information Channels
Create multiple streams of unfiltered information flowing directly from customers, frontline employees, and market touchpoints. Implement formal systems to capture observations without interpretation, including customer feedback mechanisms, competitor tracking tools, and market monitoring dashboards. Reward employees who surface uncomfortable truths rather than shooting the messenger.
3. Develop Clear Orientation Frameworks
Create simple mental models that help teams quickly make sense of incoming information. These frameworks should reflect your company’s unique market position, core competencies, and strategic objectives. Regular team discussions about how to interpret market signals will build a shared understanding that speeds up future decision cycles.
4. Map Your Decision Thresholds
Define which decisions require different levels of deliberation based on risk, reversibility, and strategic impact. For each decision type, establish clear ownership, required inputs, and maximum timeframes to prevent analysis paralysis. Document these thresholds so everyone understands when to make rapid decisions versus when more consideration is appropriate.
5. Remove Decision Bottlenecks
Identify and eliminate organizational barriers that slow down decision-making unnecessarily. Push decision authority to the lowest appropriate level where information is freshest and implementation happens. Create clear escalation paths for decisions that truly require senior input while ruthlessly eliminating bureaucratic approval steps.
6. Create Fast Feedback Loops
Design systems to quickly capture results from actions taken and feed these observations back into the OODA cycle. Track metrics that provide immediate insight into the impact of decisions without waiting for perfect data. Implement regular review sessions focused on learning from recent OODA cycles rather than assigning blame.
7. Train Decision-Making Muscles
Run regular decision-making simulations that compress the OODA Loop into shorter timeframes. These exercises should present realistic business scenarios requiring rapid assessment and action under uncertainty. Gradually increase complexity and time pressure as teams become more comfortable with the framework.
8. Build Psychological Safety
Foster an environment where teams feel secure sharing observations without fear of retribution. Leaders must model vulnerability by acknowledging their own mistakes and changing course when new information emerges. Create formal processes for challenging assumptions that reward intellectual honesty over hierarchy.
9. Integrate Technology Enablers
Implement tools that accelerate information flow and decision execution throughout your organization. Consider:
- Real-time dashboards displaying key market and operational metrics
- Collaboration platforms that break down information silos
- Automation of routine decisions to focus human judgment on higher-value choices
- Analytics capabilities that surface patterns humans might miss
10. Review and Refine Your OODA Practice
Schedule regular reviews of your OODA implementation to identify areas for improvement. Assess which decisions were made effectively and which ones should have followed a different process. Continuously refine your approach based on actual results rather than theoretical perfection.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the OODA Loop?
Every business framework has its strengths and limitations in practical application. The OODA Loop offers powerful advantages for agile companies, yet comes with challenges that must be managed.
Here’s a quick snapshot of the OODA Loop’s biggest strengths and challenges:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Speed as Competitive Edge – Enables companies to identify and act on opportunities faster than competitors, compounding long-term advantages. | Decision Quality Concerns – Rushing through cycles may lead to poor decisions based on misinterpreted data or cognitive biases. |
| Culture of Decisive Action – Encourages teams to make confident decisions with incomplete data, fostering adaptability. | Implementation Challenges – Requires strong leadership and proper information flow; hierarchical cultures may struggle with decentralization. |
| Enhanced Adaptability – Organizations quickly adjust to market changes, preventing stagnation and seizing new opportunities. | Resource Intensity – Effective observation and data processing require investments in tools and personnel, which may strain smaller businesses. |
| Improved Competitive Intelligence – Strengthens market awareness, allowing businesses to anticipate rather than react to competitor moves. | Cultural Resistance – Employees accustomed to risk-averse decision-making may struggle with the fast-paced, iterative nature of OODA. |
| Decentralized Decision-Making – Empowers frontline teams to act autonomously, increasing engagement and execution speed. | Strategic Consistency Issues – Frequent tactical shifts can cause confusion and misalignment with long-term goals. |
Key Advantages
Now, Let’s take a much closer look at how these factors play out in practice—why its advantages can be game-changers and how to navigate its potential drawbacks.
Speed as Competitive Edge
Companies that cycle through observation to action faster than competitors can identify and exploit market opportunities before others even notice them. This advantage compounds over time as your organization develops institutional muscle memory for rapid iteration and adaptation. The fastest OODA practitioners can execute multiple decision cycles while competitors are still gathering data.
Culture of Decisive Action
The framework creates a culture of decisive action rather than endless analysis. Teams learn to make confident decisions with incomplete information instead of waiting for perfect data that never arrives. Organizations using OODA principles develop adaptability as a core competency, allowing them to navigate disruption more effectively than rigid competitors.
Enhanced Adaptability
OODA-driven organizations respond to market changes with remarkable agility and minimal friction. Teams become comfortable with continuous adaptation rather than rigid adherence to outdated plans. This flexibility allows businesses to capitalize on emerging opportunities while avoiding threats that sink less responsive competitors.
Improved Competitive Intelligence
Organizations implementing the OODA Loop develop superior observation capabilities that capture valuable market insights. These enhanced intelligence systems detect subtle shifts in customer behavior and competitive activity before they become obvious trends. Companies gain the ability to anticipate competitive moves rather than merely reacting to them after the fact.
Decentralized Decision-Making
The OODA Loop naturally pushes decision authority to frontline teams closest to customers and market realities. This decentralization speeds execution and increases employee engagement through greater autonomy. Organizations benefit from the collective intelligence of their entire workforce rather than relying solely on top-down directives.
Potential Drawbacks
Despite its powerful benefits, the OODA Loop introduces several challenges that must be actively managed. Organizations should be aware of these pitfalls before implementation.
Decision Quality Concerns
The OODA Loop can create decision fatigue when overused for minor issues that don’t require rapid cycling. Organizations sometimes rush through the orientation phase, leading to hasty decisions based on misinterpreted data or unconscious biases. The constant pressure to speed up decision cycles may create stress and burnout among teams not properly trained or supported.
Implementation Challenges
The framework demands significant leadership attention to ensure quality observations feed the system. Companies with hierarchical cultures may struggle to implement OODA principles if leaders hoard information or punish bearers of bad news. Without proper documentation of decisions and outcomes, organizations lose valuable learning opportunities that could improve future OODA cycles.
Resource Intensity
Maintaining effective observation systems requires substantial investment in tools and personnel. Small businesses may lack the resources to gather and process information at the speed needed for optimal OODA execution. The organizational energy required to maintain rapid OODA cycling can detract from other important business activities.
Cultural Resistance
Established organizations often face significant resistance to the faster tempo and higher uncertainty tolerance required by the OODA Loop. Employees accustomed to thorough analysis and risk avoidance may feel uncomfortable with the framework’s emphasis on speed and iteration. Leadership must actively manage this cultural shift to prevent regression to slower decision patterns.
Strategic Consistency Issues
Rapid OODA cycling can sometimes lead to strategic inconsistency if not properly aligned with longer-term objectives. Frequent tactical shifts might create confusion about organizational priorities and direction. Companies must balance OODA responsiveness with strategic continuity to avoid erratic execution patterns that confuse customers and employees.
Taking Action: Your OODA Loop Journey Starts Now
Mastering the OODA Loop transforms your business from reactive to proactive, giving you the agility to outmaneuver competitors regardless of company size. Implementing this framework requires commitment to faster decision cycles, psychological safety for honest observations, and systems that capture rapid feedback.
Start with one business domain today, apply these principles consistently, and watch how your team develops the decisive edge that defines market leaders in unpredictable environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the OODA Loop differ from other decision-making frameworks like Six Sigma?
Unlike Six Sigma’s focus on eliminating defects through detailed analysis, the OODA Loop prioritizes speed and adaptability over perfection. Six Sigma works well for stable processes with ample data, while OODA excels in rapidly changing environments where quick action trumps exhaustive analysis.
Can startups benefit from the OODA Loop despite limited resources?
Startups are actually ideal candidates for OODA implementation due to their inherent agility and fewer bureaucratic layers. Their smaller size enables faster information flow and decision execution, creating natural advantages against larger competitors who typically struggle with organizational inertia and risk aversion.
How do you measure the effectiveness of your OODA Loop implementation?
Track metrics like decision cycle time, implementation speed, and business outcomes compared to pre-OODA benchmarks. Effective implementation typically shows decreased time between opportunity identification and action, increased proactive decisions, and improved ability to capitalize on emerging market trends before competitors.
Related:
- PDCA Cycle: A Proven Strategy for Continuous Improvement
- How to Scale Your Business with Strategic Moves
- Art of War in Business: Tactics for Market Leadership
We empower people to succeed through practical business information and essential services. If you’re looking for help with SEO, copywriting, or getting your online presence set up properly, you’re in the right place. If this piece helped, feel free to share it with someone who’d get value from it. Do you need help with something? Contact Us
Want a heads-up once a week whenever a new article drops?







