Imagine you’ve spent countless hours and resources developing an app or service that you’re sure will take the market by storm. Then, the launch day arrives, and users flock to your platform in droves.
That’s a success, right? Not quite. Then, fast forward a few weeks, and you notice a sharp decline in active users. What went wrong?
Welcome to the world of user retention, where keeping users engaged is just as crucial as attracting them in the first place. As businesses increasingly shift to digital platforms, understanding and mastering user retention has become a make-or-break factor for long-term success.
Ready to unlock the secrets of keeping your users coming back for more? Let’s jump right in.
What is User Retention?
User retention refers to the ability of a company or product to keep its users engaged and coming back over time. It’s a metric that measures how well you’re holding onto your users after they’ve signed up or made their first purchase. Think of it as the digital equivalent of customer loyalty in the brick-and-mortar world.
But why does it matter so much?
User retention indicates the health and viability of a product. Getting people to sign up or make an initial purchase is one thing. But keeping them coming back, engaging with your product, and repeatedly finding value in it is far more important.
By focusing on retention, you’re making the most of the users you’ve already worked hard to attract. Plus, retained users are more likely to become brand advocates, spreading the word about your product or service to others.
Why is User Retention Important?
Let’s go into more detail about why user retention is important and why it should be at the top of your priority list as a digital product creator or service provider.
Cost Efficiency
Acquiring new users is significantly more expensive than retaining existing ones. Various studies suggest that attracting a new customer costs five times more than keeping an existing one.
This difference is due to the marketing, advertising, and sales efforts required to attract new users, which can be costly compared to the relatively lower costs of maintaining relationships with current users.
Revenue Growth
Typically, returning users generate more revenue than new users. This is because repeat users are more likely to purchase additional products, subscribe to premium services, or engage in other revenue-generating activities.
In addition, loyal users often have higher lifetime value (LTV), contributing more to your bottom line.
Customer Insights
Long-term users provide invaluable insights into what’s working and what isn’t. They are more likely to give feedback, participate in surveys, and share their experiences.
This feedback loop is crucial for making data-driven improvements to your product or service, ensuring it meets your users’ evolving needs.
Brand Loyalty
High retention rates are a strong indicator of brand loyalty. Loyal users are likelier to recommend your product to others, creating a virtuous organic growth cycle through word-of-mouth.
This loyalty can be a significant competitive advantage, helping you stand out in a crowded marketplace.
How Do You Measure User Retention?
Measuring user retention involves various methods and metrics that provide insights into user behavior and engagement levels. Here are some key ways to measure user retention:
1. Retention Rate
The retention rate is the most direct measure of user retention. It calculates the percentage of users who continue to use your product over a specified period. The formula is straightforward:
Retention Rate=
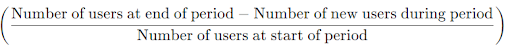
For example, if you start with 1,000 users at the beginning of the month, gain 200 new users, and end with 900 users, your retention rate would be:
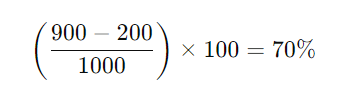
2. Churn Rate
The churn rate is the inverse of the retention rate and measures the percentage of users who stop using your product within a given period. To calculate churn rate:

A lower churn rate indicates better retention. For instance, if you start with 1,000 users and lose 100, your churn rate would be:

3. Cohort Analysis
Cohort analysis involves grouping users based on shared characteristics, such as their sign-up date, and tracking their behavior over time. This method lets you see how user segments interact with your product and identify trends.
For example, compare the retention rates of users who signed up after a significant update versus those who joined before to see if the update positively impacted retention.
4. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV measures the total revenue expected from a single user account over its lifespan. It helps you understand the long-term value of retaining a user.
Higher CLV indicates that your retention strategies effectively generate more revenue from each user.
5. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
NPS gauges user satisfaction and loyalty by asking users how likely they are to recommend your product to others.
Users respond on a scale from 0 to 10, and those who score 9 or 10 are considered promoters. A high NPS correlates with high retention rates, as satisfied users are likelier to continue using and recommending your product.
What Drives User Retention?
Understanding what keeps users coming back is key to improving retention. Some factors that drive user retention include:
- Onboarding: Retaining users begins with a smooth onboarding process. Users must easily set up their accounts and complete critical steps, such as integrations or inviting teammates, as quickly as possible.
- Activation: After onboarding, users need to see immediate benefits from the product. Early successes motivate users to keep coming back.
- Habit: Creating habits that encourage users to return regularly is essential. This could be triggers that prompt them to complete tasks, like taking a photo of a receipt for an expense app. Understanding how often users naturally use the product helps shape the onboarding and activation strategies.
For example, the team at Oranj noticed that their retained customers frequently used the platform and completed onboarding.
By analyzing where users dropped off during onboarding, they improved the process, increasing completion rates and boosting retention.
User Retention vs. Customer Retention
- User Retention: Focuses on individuals who use the product regularly (usage metric).
- Customer Retention: Focuses on the accounts that pay for the product (financial metric).
These terms are usually the same for consumer companies because the user and the payer are often the same person.
User Retention Rates vs. Churn Rates
- User Retention Rates: Measure how many users return to a product within a specific time frame.
- Churn Rates: Measure how many users stop using the product within that same time frame.
While they are opposite measures, companies often prefer to focus on retention rates because they provide a positive outlook and help identify areas for improvement.
Choosing the right time frame for measuring these rates is essential based on how frequently the product is used. For example, a daily-use product needs a shorter time frame, while a monthly-use product needs a longer one.
How to Improve the User Retention?
Improving user retention is crucial for sustained growth. Below are detailed tips on achieving this through exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, and loyalty programs.
Enhance Onboarding
A smooth and informative onboarding process helps new users quickly understand and appreciate your product, reducing the risk of early churn. Effective Onboarding can include in-app tutorials, interactive walkthroughs, and helpful tooltips that guide users through the key features of your product.
For example, a new fitness app user might benefit from a guided tour highlighting how to set goals, track progress, and join community challenges.
Personalize User Experience
Personalization tailors the user experience based on individual preferences and behaviors. This approach makes users feel valued and understood, increasing satisfaction and engagement.
Personalization can range from personalized content recommendations to customized user interfaces. For instance, an e-commerce site might recommend products based on a user’s past purchases and browsing history.
Engage Regularly
Keeping users engaged requires regular communication and updates. Email, push notifications, and in-app messages inform users about new features, special offers, or relevant content.
However, it’s essential to strike a balance to avoid overwhelming users with too many messages. For example, a news app might send daily summaries of top stories, while a gaming app might notify users about new levels or challenges.
Gather and Act on Feedback
Regularly solicit user feedback through surveys, reviews, and direct interactions. Act on this feedback to improve and show users that their opinions matter. This feedback loop helps improve the product and fosters community and user loyalty.
For instance, a software company might release regular updates based on user feedback to fix bugs and add requested features.
Implement Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs reward repeat users with points, discounts, or exclusive offers, incentivizing ongoing use. These programs can take various forms, such as point systems, tiered memberships, or referral bonuses.
For example, a coffee shop app might offer a free drink for every ten purchases, and a travel app might provide early access to sales and special rates for frequent travelers.
Optimize User Interface
A well-designed, intuitive user interface (UI) enhances user satisfaction and retention. Ensure your product is easy to navigate and has a clean and responsive design. Regularly test and refine the UI to remove friction points that might frustrate users.
For example, a finance app should have a straightforward layout that allows users to quickly check their balances, make transfers, and view transaction histories.
Utilize Analytics Tools
Leverage analytics tools like Google Analytics to track user behavior and retention metrics. These tools provide insights into how users interact with your product, highlighting areas for improvement.
For instance, you might discover that users frequently abandon a particular feature, prompting you to investigate and address any underlying issues.
Conduct Cohort Analysis
Cohort analysis helps you understand which user segments are more likely to stay and why. Use this information to focus your efforts on the most valuable user groups. For example, a streaming service might find that users who create custom playlists are likelier to remain subscribed, prompting them to enhance and promote this feature.
Improving user retention is an ongoing process that requires a deep understanding of your users and a commitment to providing continuous value. You can achieve sustainable growth and long-term success by focusing on user retention.
Master User Retention for Lasting Success
User retention is a critical factor in the long-term success of any digital product or service. By understanding what it is, why it matters, and how to measure and improve it, you’re setting yourself up for sustainable growth and success.
Boosting your user retention rates won’t happen overnight. It requires ongoing effort, analysis, and optimization. But with the right strategies in place, you can create a product that not only attracts users but keeps them coming back time and time again.
We empower people to succeed through practical business information and essential services. If you’re looking for help with SEO, copywriting, or getting your online presence set up properly, you’re in the right place. If this piece helped, feel free to share it with someone who’d get value from it. Do you need help with something? Contact Us
Want a heads-up once a week whenever a new article drops?







