Key advancements in NLP (natural language processing) are helping machines understand human language better, which has changed SEO forever. This article explores those NLP developments and how we can leverage them for SEO.
SEO has largely been about using keywords in a way that makes it easy for artificial intelligence (AI) to understand copy. While that hasn’t changed, today’s AI is more sophisticated and can understand context much better, thanks to advancements in language processing. These developments have changed SEO.
The Internet has way more information than it did a decade ago. Millions of new content are published daily and search engine algorithms need to process all of it. To interpret all that data, AI needs to structure the information in a rational database. But AI has a problem with the ambiguity in human language.
When we speak or express ourselves, the words we use, the order in which they are used, and our tone, can alter interpretation plus value. Communication can carry different meaning and AI has a tough time understanding certain statements. This is where NLP comes in.
NLP helps computers make sense of human language in a valuable way. Machine Learning or deep learning (AI learning methods) applied to NLP can discern patterns, figures of speech, entities, and positive or negative sentiments.
What Exactly is NLP?
NLP is a subfield of AI that studies the interaction between human beings and computers. NLP aims to help computer programs (e.g. search algorithms) read, understand, and make sense of our language.
How Search Engines Use NLP
The technology allows search engines to rely less on keyword frequency and more on context comprehension. In other words, their algorithms can better understand your web copy. For example, AI knows that the word ‘winners’ refers to persons, and the term ‘new sites’ could refer to new locations or website platforms.
When we do a quick search for the latter term, you can see that Google returns two types of results at the top. The first involves creating websites and the second shows ‘top stories’ relating to real-world locations.
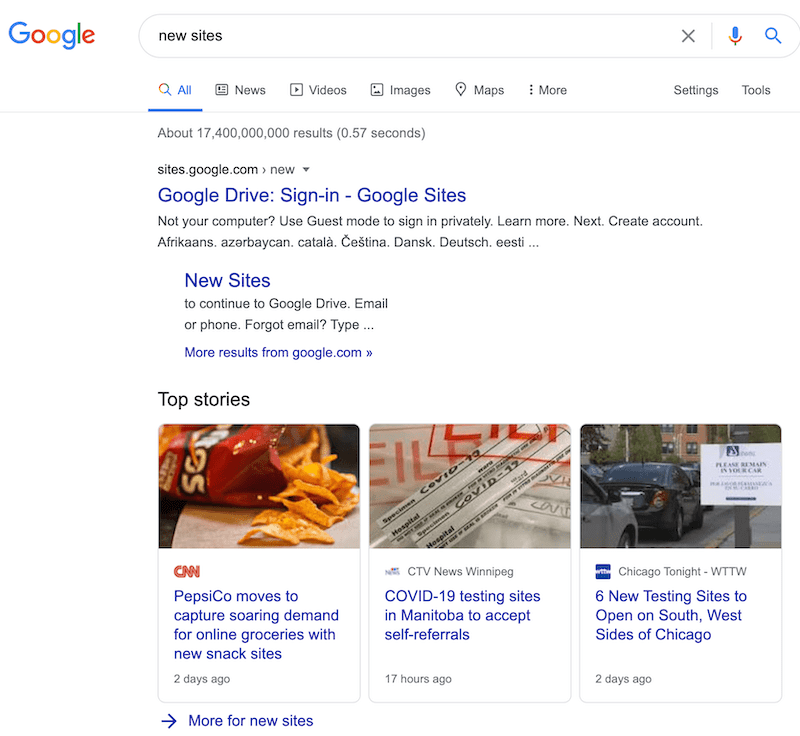
The algorithm diversified the search results because it knows that the term ‘new sites’ can mean different things. But this is only one way that search engines use NLP.
AI can also convert video audio into text and extract meaning from the information. YouTube may already be doing this as an additional way to rank videos. We can see some evidence of this in some Google searches that return video results.
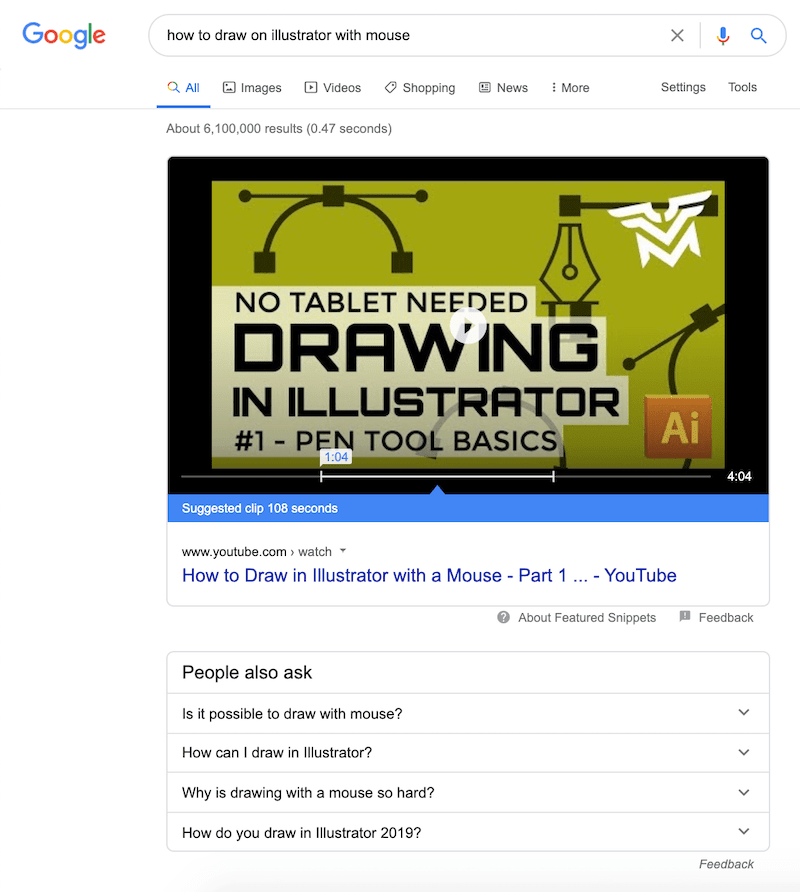
The algorithm makes suggestions on where the user should start watching a video to get the answers that they want fast. The screenshot above is an example of that in action (right below the video, it reads “suggested clip 108 seconds”). The creator did not have to specify that information in the video description.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a sub-field of NLP. It is the process of interpreting and classifying the emotions behind words or sentences. Each sentence is rated as negative, positive, or neutral. Search engine algorithms use this to understand the sentiments behind articles, customer reviews, landing pages, etc.
You can see evidence of sentiment analysis used on featured snippets. These are short snippets of text that search engines use to answer user queries quickly.
For example, when we search for the term ‘are birds good pets,’ the following comes up.
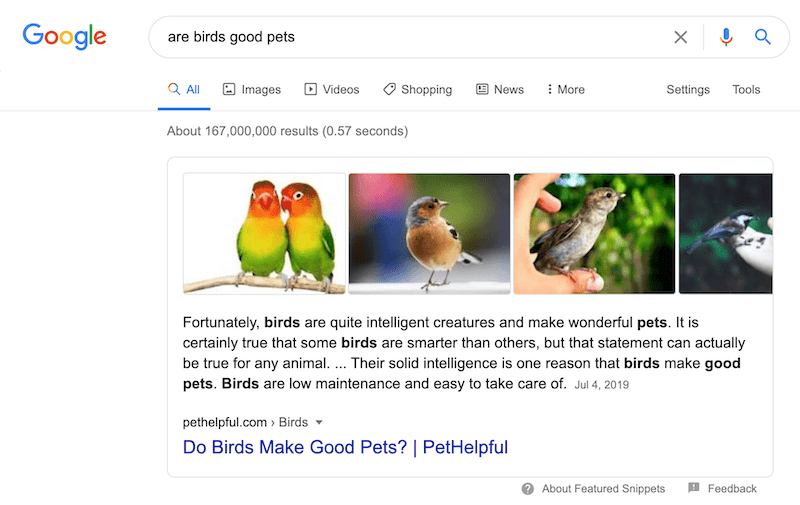
When we alter the term slightly and search for ‘are birds bad pets,’ we get the following.
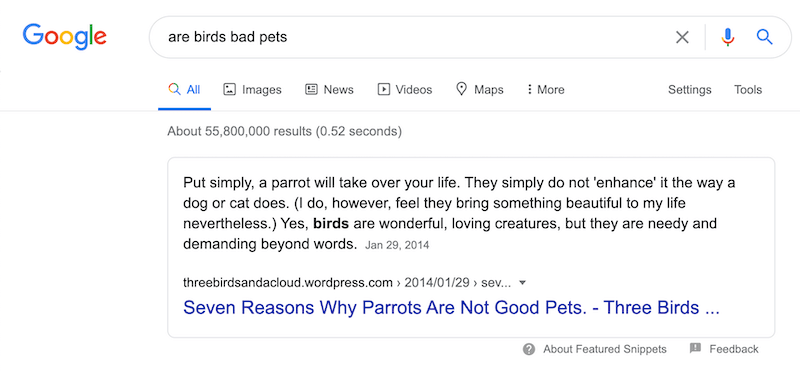
Notice that the algorithm is returning featured snippets based on sentimental value. One snippet focuses on why birds are good pets; the other explains why they can suck as pets.
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)
BERT is the latest NLP pre-training model by Google, officially announced last year. The search giant is committed to improving how it uses NLP to enhance search, and BERT is a product of that goal.
BERT enables the processing of words in relation to everything in a given sentence, instead of one-by-one and in order. That means it can extract context from not just the words but also everything that comes before and after the copy.
The implementation of BERT has tremendously improved the accuracy of search results. Both Bing and Google can comprehend searcher intent much better. Also, worth noting is that Bing started using BERT months ahead of the official Google announcement.
Leveraging NLP Developments
Here’s how to leverage these developments in NLP to improve SEO outcomes.
1. Watch the Sentiment
We have to start minding the sentiment used in our copies since NLP AI isn’t perfect, yet. For every article, think about the target audience and what you want them to feel. For example, “why work with us?”, can be construed as a negative sentiment while “reasons to work with us,” is more positive.
That is what happened when the two statements were analyzed using Google’s NLP demo (a score between 0.25 and 1.0 is positive).
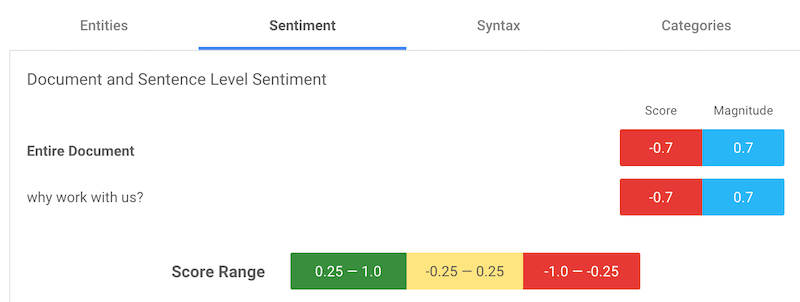
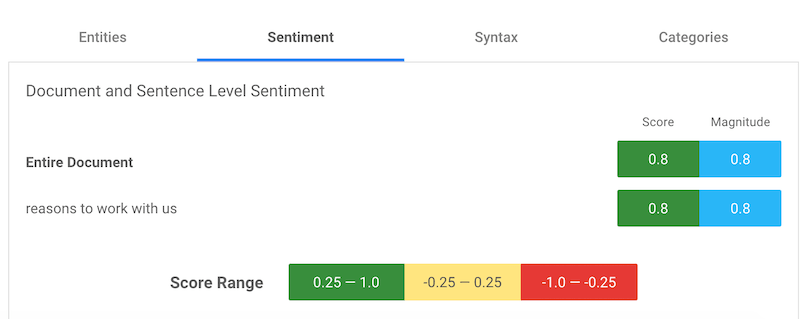
The question to ask each time is:
- Which web pages are ranking for the target keyword and what’s the overall sentiment?
Always analyze the SERP (search engine results pages) before creating your content. That’s because you may find it tough to rank #1 on a SERP with lots of positive sentiment pages. For the most part, search algorithms are programmed to give users more of what they want.
2. BERT Gets Stop Words
‘Stop words’ or prepositions are commonly used words that NLP algorithms typically filter out before or after processing text. NLP training models don’t usually understand how ‘stop words’ fit with the meaning of a sentence. BERT, however, can make sense of stop words.
Here’s what the VP of search, Pandu Nayak, noted on Google’s official BERT announcement.
“Particularly for longer, more conversational queries, or searches where prepositions like “for” and “to” matter a lot to the meaning, Search will be able to understand the context of the words in your query. You can search in a way that feels natural for you.”
It’s common SEO practice to remove stop words from URL slugs. However, it may be best to leave them, providing that they’re necessary. For instance, an article about ‘how to play basketball’ can be left as your-domain/how-to-play-basketball/. Usually, we would change the URL to your-domain/play-basketball/. But no need to remove the stop words since they are a context necessity.
‘Play basketball’ and ‘how to play basketball’ have different intents. For the former, the user might want to find a place to play basketball. For the latter, it’s quite clear that the user wants to learn how to play basketball.
3. More Ranking Opportunities
Now that search engines can understand the meaning behind search queries better than ever; you have more opportunities to rank. That is because their algorithms should return more relevant search results. We should see fewer instances where powerful domains outrank much more relevant web pages to the user’s intent. As a result, smaller websites have more opportunities to rank for underserved search terms.
You can also play around with the intent of your content ideas a bit more. You may see better results from niche down content such as “math tutoring for grownups” vs. “math tutoring.”
4. More Featured Snippets
More featured snippets can be positive or negative, depending on where you stand. But we may see even more featured snippets on search results after the BERT update due to AI’s increased understanding of content.
A study by Ahrefs found that featured snippets receive fewer clicks than the ranking web page below them. The same study also found that the presence of featured snippets, in general, reduce CTR (click-through-rate).
But while featured snippets can reduce CTR, they may improve it in some industries. Also, featured snippets may improve brand awareness over time. You’ll need to append the brand’s name to your SEO titles to use the SERP for brand awareness. This way, when users come across a web page on a featured snippet, they’ll also see your brand name.
All in all featured snippets should increase as NLP advances.
5. Naturally-written Content Will Perform Better
The common consensus among SEOs is that you can’t optimize content for BERT, and that’s true. But you can write more naturally.
You see, BERT enhances NLP in ways that others before it could not, therefore, improving AI’s understanding of natural human language. So your content should perform better on the SERPs if you write more naturally. And the following tweet by Danny Sullivan, Google’s public Search Liaison, confirms that idea.
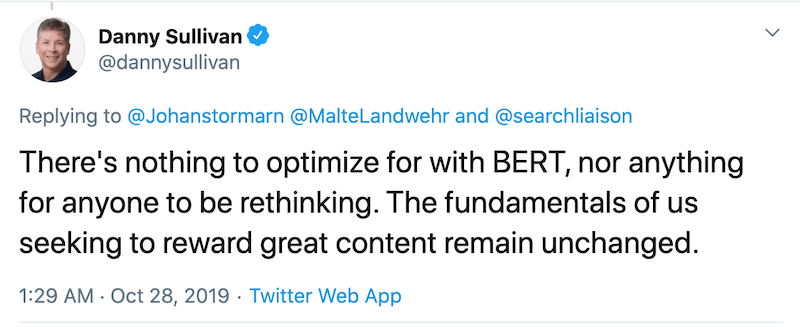
6. Categorization is Key
AI needs to associate your content with the right category. That should improve the rank of your web page and right now, you can use Google’s NLP demo (link provided earlier) to check.
Copy and paste all your text (including navigation link texts and image alternative texts) into the box, then click ‘Analyze.’
The system will give your content a confidence score between 0 and 0.99. A high score means AI is very confident.

Think Long-term
NLP is advancing at a fast pace and that’s a good thing for SEO. We just have to approach SEO from a long-term perspective. AI learns fast, so every loophole is discovered and closed quickly. As a result, relying on cheap SEO tricks don’t work for long.
We need to think of SEO as what it is – a marketing discipline. Know your target audience, understand the buyer’s journey, and meet consumer needs accordingly. When you approach SEO with a long-term perspective, you don’t panic every time a new Google update rolls out.

I’m a freelance copywriter and SEO specialist. I aim to empower individuals and businesses with impactful marketing solutions and insights. In my downtime, I recharge by embracing the beauty of nature or cherishing moments with my loved ones. If you found value in this post, please consider sharing it.
Want a heads-up once a week whenever a new article drops?







